
Each of these formatting definitions can be turned on or off.Ĭonditional formatting is a format such as cell shading or font color that a spreadsheet can apply automatically to cells if a specified condition is true. Each table style is made up of a collection of formatting definitions, each of which corresponds to a particular region of the table-e.g., whole table, first column stripe, first row stripe, first column, header column, first header cell, etc.
Note also that not only is the style specified, but the specification also tells us which aspects of the style are turned on (e.g., showRowStripes="1") and which are turned off (e.g., showLastColumn="0"). For example, the following sample table definition specifies the TableStyleMedium9 style. Table-Level FormattingĪ table applies a table style by specifying a element within the table definition in the tables part.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/36-openoffice-calc-basic-spreadsheet-tutorial-599f0be867e9479f8773977cfbcc979e.jpg)
In this case they are the same, so there is no difference anyway. The formatting of the style is same as the direct formatting, and the attributes applyNumberFormat, applyBorder, applyAlignment, and applyProtection, each with values of 0, tell us not to apply the corresponding values of the style but instead apply the values for the direct formatting. (Remember that it is a zero-based index.) We know from the type attribute for the cell t="s" that the text is stored in the shared strings part, and from we know that string is the 26th string or. Let's look at the XML for the first cell in row 13 of the worksheet part. This formatting is done within the shared string part where the text of the cell is stored. Obviously this cannot be accomplished with a cell style. For example, see cell A13 below, with blue color for the first word and orange underline for the second. Text-Level Formattingīefore getting to the styles applied to a worksheet, however, let's first cover formatting at the text level, that is, not formatting applied to the entire cell, but formatting that might change from word to word, such as different colors or effects. A style or formatting element can define a color, font, or effect by referencing a theme, but of course that format may change if the thme is changed. Themese define a set of colors, font information, and effects on shapes. Pivot table styles specify formatting for regions of a pivot table, such as colors for totals or for the row axis.
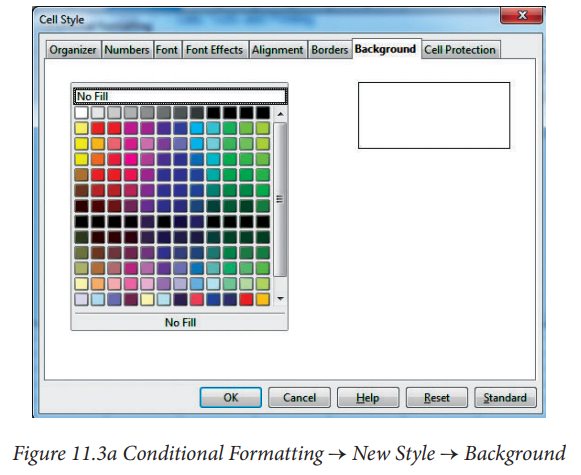
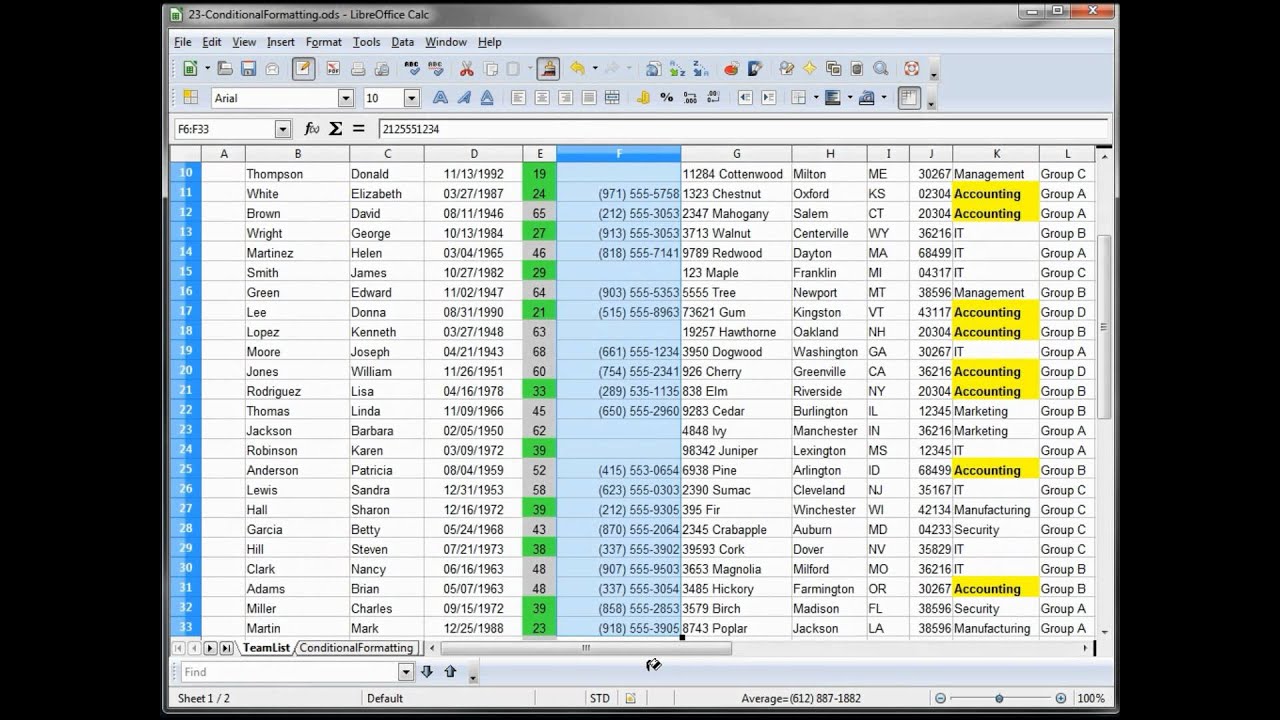
Table styles specify formatting for regions of a table, such as, e.g., headers are bold or a gray fill should be applied to alternating rows. There is also a single theme part for the entire workbook.Ī cell style can specify number format, cell alignment, font information, cell borders, and background/foreground fills. The formatting is always stored separately within a single styles part for the workbook. However, unlike in WordprocessingML, styling XML never appears with the content in a worksheet. There are cell styles, table styles, and pivot styles. Then enter a formula that will return TRUE for conditions you're testing.Spreadsheets can be styled using styles, themes, and direct formatting. First, select the cells you want to format. This example is quite simple example, but the approach is the same for more complex rules. Now, if I don't need the first rule, I can simply remove it. You can see that the highlighted names match the average scores highlighted by the first rule. When I save the rule, names where the average in column H is less than 80 are highlighted I don't need to lock the column in this case, because the relative position of names in column B to the averages in column H won't be changing. Note that H6 corresponds to the active cell in this selection, which is B6. This will return true when the average is less than 80 and trigger the rule. Next, select "New Rule" from the Conditional Formatting menu on the home tab of the ribbon, and select the option to use a formula.įor the formula itself, start with an equal sign. Start by selecting the cells you want to format. In that case, you'll need to apply conditional formatting with a formula. For example, if I want to highlight the average test scores in column H that are below 80, I can just select the cells and apply a Conditional Formatting rule with that logic.īut what if you want to highlight the names in column B when the average is below 80 in column H. The easiest way to apply conditional formatting is to apply rules directly to the cells you want to format.
Openoffice conditional formatting refer to cell above how to#
In this video, we'll look at how to apply conditional formatting to one cell based on values in another, using a formula.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
